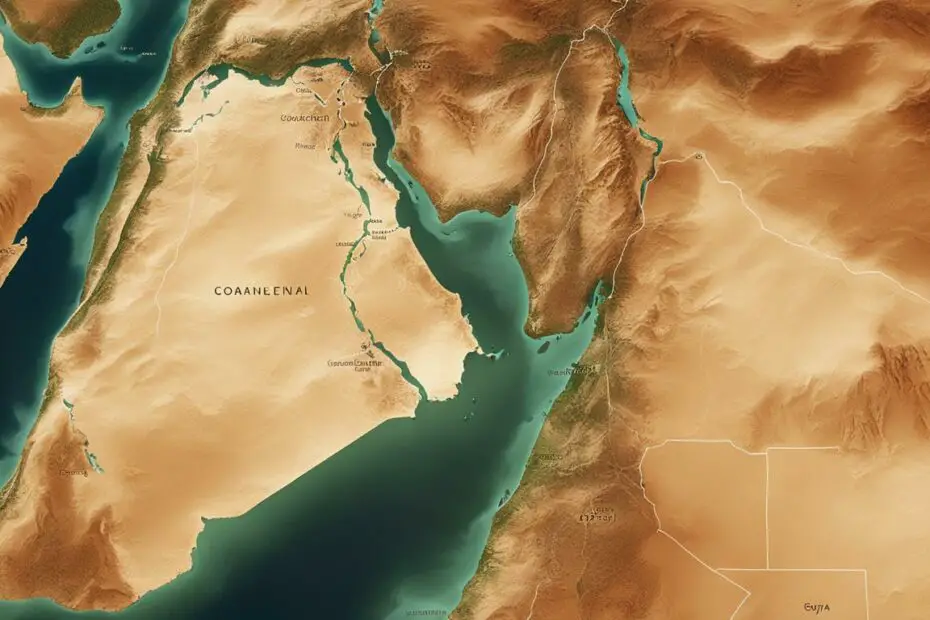
Egypt’s geographical location has long been a topic of discussion when it comes to its regional affiliation. Many people wonder, “Is Egypt in the Middle East?” In this article, we will explore the facts and insights surrounding Egypt’s position in the Middle East.
The term “Middle East” is a dynamic geographic designation that has evolved over time. Originally coined by the British in the late 19th century, the Middle East was defined as the region between the Near East and the Far East. However, as regional boundaries have shifted, the Middle East now encompasses a broader area.
In its most common definition, the Middle East includes Egypt in the west, Iran in the east, the Arabian Peninsula in the south, and Turkey in the north. However, different sources and organizations may have varying definitions, sometimes including or excluding certain countries.
Egypt’s geographical location places it within the Middle East region. Situated in northeastern Africa, Egypt spans both the African and Asian continents. The Sinai Peninsula, which connects Egypt to Asia, has historically played a crucial role in shaping its regional affiliation.
Furthermore, Egypt’s historical, cultural, and political connections with other Middle Eastern countries have solidified its relationship with the region. Egypt is a founding member of the Arab League and has been involved in various regional issues and conflicts throughout its history.
While there may be debate and fluidity regarding regional boundaries, Egypt’s position in the Middle East is firmly established. Its geographic location, historical ties, and participation in regional organizations all contribute to its regional affiliation. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore Egypt’s relationship with the Middle East, its population and demographics, its digital transformation, and its role in the changing dynamics of the Middle East.
Geographical Position of Egypt
Egypt is strategically located in northeastern Africa, encompassing both the African and Asian continents. The majority of Egypt’s landmass is situated in Africa, while the Sinai Peninsula forms a land bridge connecting it to Asia. This unique geographical location places Egypt at the crossroads of three major regions: Africa, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean.
Geopolitically, Egypt is often classified as part of the Middle East due to its close proximity to other Middle Eastern countries and its historical, cultural, and political ties with the region. Its position as a gateway between Africa and Asia has played a significant role in shaping its regional affiliation and influence.
| Action | African Continent | Middle East | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Egypt is positioned at the crossroads of the three major regions. | Mainly located in Africa, with a small part (Sinai Peninsula) connecting to Asia. | Considered part of the Middle East due to its proximity and historical ties. |
| Regional Affiliation | Egypt has strong affiliations with both the African continent and the Middle East region. | Historically, culturally, and politically connected to Africa. | Historical, cultural, and political ties with the Middle East. |
| Strategic Importance | Egypt’s geographic position provides it with significant strategic importance. | Acts as a gateway between Africa and the Middle East. | Located near other Middle Eastern countries, shaping its regional influence. |
Egypt’s Relationship with the Middle East
Egypt has a long-standing relationship with the Middle East region. As a founding member of the Arab League, an organization that promotes cooperation among Arab countries, Egypt has played a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the region. Throughout its history, Egypt has been deeply involved in various regional issues and conflicts, including the Arab-Israeli conflict and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
In 1979, Egypt made a significant stride in regional diplomacy by signing a historic peace treaty with Israel, becoming the first Arab country to establish diplomatic relations with its neighbor. This landmark agreement signaled Egypt’s commitment to seeking peace in the Middle East and opened doors for further dialogue and cooperation.
Despite shifts and changes over time, Egypt remains an important player in the Middle East. Its regional affiliation is rooted in its geographical position and historical ties with neighboring countries. Egypt’s influence extends beyond political and diplomatic circles, encompassing cultural, economic, and social connections with other Middle Eastern nations.
Throughout the years, Egypt has actively participated in regional initiatives, fostering collaboration and unity among Arab nations. Its engagement in issues such as counterterrorism, regional stability, and the promotion of Arab identity highlights its dedication to shaping a positive future for the Middle East.

| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Egypt’s Role in the Arab League | Egypt is a founding member of the Arab League, demonstrating its commitment to cooperation and unity among Arab countries. |
| Peace Treaty with Israel | In 1979, Egypt signed a historic peace treaty with Israel, becoming the first Arab country to establish diplomatic relations with its neighbor. |
| Geographical and Historical Affiliations | Egypt’s position in the Middle East is reinforced by its geographical proximity to other Middle Eastern countries and its longstanding historical connections with the region. |
| Regional Engagement | Egypt actively participates in regional initiatives, addressing issues such as counterterrorism, regional stability, and the promotion of Arab identity. |
Population and Demographics
Egypt is home to a vast and diverse population, making it the most populous country in the Middle East and the third most populous in Africa. With a population of over 100 million, Egypt’s demographics play a crucial role in shaping the nation’s economy, social development, and political stability. Understanding the population composition and trends is essential for policymakers, businesses, and organizations operating in Egypt.
The Youthful Population
One striking characteristic of Egypt’s population is its youthfulness. Around 40% of Egyptians fall between the ages of 10 and 20 years, and two-thirds of the population is under the age of 29. This young demographic presents both opportunities and challenges for the country.
The youth bulge in Egypt’s population offers potential for economic growth and innovation as this cohort enters the workforce. However, it also poses challenges in terms of providing education, healthcare, and employment opportunities for the growing youth population. Addressing these challenges is crucial to harness the demographic dividend and ensure a prosperous future for Egypt.
Projected Population Growth
With its high birth rate and substantial youth population, Egypt’s total population is expected to grow significantly in the coming decades. By 2050, the population is projected to reach 150 million, further straining resources and infrastructure. Policymakers need to plan accordingly to meet the needs of a growing population while ensuring sustainable development.
The image presents a visually appealing overview of Egypt’s population and demographics, depicting the growth and age distribution trends. It provides a graphical representation of the significance of the youthful population and the projected population growth, enhancing understanding and analysis of Egypt’s demographic landscape.
In conclusion, Egypt’s population and demographics are critical factors that shape the nation’s present and future. The youthful population offers opportunities for economic growth, but also necessitates investments in education and employment opportunities. The projected population growth calls for strategic planning to address the challenges of providing essential services and infrastructure for a larger population. By understanding and leveraging these demographic trends, Egypt can pave the way for a prosperous and sustainable future.
Digital Transformation in Egypt
Egypt has undergone a remarkable digital transformation in recent years, positioning itself as a rising player in the digital landscape. With an internet penetration rate of around 50%, there is significant room for further growth and adoption of digital technologies. The country’s mobile connections account for a staggering 93% of the population, indicating a strong reliance on mobile devices and technology.
Several factors have contributed to Egypt’s digital transformation. Improved infrastructure has paved the way for enhanced connectivity and faster internet speeds, enabling more Egyptians to access the digital realm. Additionally, the availability of cheaper data packages and more affordable smartphones has made online accessibility more attainable for a larger portion of the population.
This digital revolution has created numerous opportunities for both international and domestic operators. Companies have been increasingly investing in Egypt’s digital infrastructure, recognizing the country’s potential for growth and profitability. With a population of over 100 million people, Egypt represents a vast and untapped market for digital services and innovations.
As Egypt continues to embrace the digital age, the country is witnessing a surge in online activities. E-commerce platforms are gaining traction, and digital payment solutions are becoming more prevalent. This shift towards digital transactions has the potential to revolutionize the economy by streamlining and modernizing financial processes.

In conclusion, Egypt’s digital transformation is well underway, with the country embracing the opportunities and advancements offered by the digital age. The increasing internet penetration rate and mobile connectivity present a promising landscape for businesses and individuals alike. As Egypt continues to invest in its digital infrastructure and foster an environment of innovation, the nation is poised to become a thriving digital hub in the Middle East and beyond.
Fintech and E-commerce Potential
Egypt’s digital ecosystem is experiencing rapid growth, paving the way for exciting opportunities in the fintech and e-commerce sectors. With a high rate of mobile penetration and increasing adoption of digital financial services, the country is poised for the development of a robust fintech market. This presents a unique chance to expand access to financial services, particularly for the large unbanked population, and contribute to the reduction of poverty rates in Egypt.
The e-commerce landscape in Egypt is also set to flourish, driven by the continuous growth of internet penetration and the rising demand from consumers. While cash on delivery remains a popular payment method for online purchases, there is a noticeable shift towards digital payments and online transactions. This trend reflects the changing consumer preferences and the increasing convenience and security provided by digital payment platforms.
Key Factors Contributing to Fintech and E-commerce Growth in Egypt
- Mobile Penetration: Egypt boasts a high mobile penetration rate, with mobile connections covering approximately 93% of the population. This widespread mobile usage provides a strong foundation for the growth of fintech and e-commerce services, as more individuals gain access to digital platforms.
- Digital Financial Services: The increasing adoption of digital financial services, such as mobile banking and digital wallets, creates a conducive environment for fintech innovation. These services offer increased convenience, speed, and accessibility, attracting more users and promoting a cashless economy.
- Internet Penetration: Egypt’s internet penetration rate has been steadily rising, opening up vast opportunities for e-commerce growth. As more individuals gain internet access, the potential customer base for online retailers expands, fueling the demand for e-commerce services and products.
- Consumer Demands and Behavior: Changing consumer expectations and preferences drive the transformation of the e-commerce landscape in Egypt. Consumers are increasingly seeking convenience, personalized experiences, and secure payment methods, all of which contribute to the growing adoption of online shopping and digital payments.
Egypt’s Role in the Changing Middle East
Egypt’s strategic position in the Middle East has positioned it as a key player in the region’s ever-evolving dynamics. In recent years, Egypt has experienced significant shifts in its alliances and approach, shaping its role in the changing Middle East. One notable development is the country’s cooperative relationship with Israel, demonstrating a new dynamic that has emerged.
Collaboration between Egypt and other Arab states in the region highlights shared concerns regarding Iran’s regional influence and the threat posed by jihadist groups. As Egypt aligns itself with its Sunni Arab partners, opportunities for regional cooperation arise. These changing dynamics and the need for collaborative efforts present Egypt with the chance to play a significant role in shaping the future of the Middle East.
In the midst of the Trump administration’s formulation of Middle East policy, the establishment of a pragmatic bloc comprising Egypt, Saudi Arabia, other Gulf states, and Israel is perceived by some as a desirable development. As this potential alliance takes shape, it could have far-reaching implications for the region.
FAQ
Is Egypt considered part of the Middle East?
Yes, Egypt is considered part of the Middle East due to its proximity to other Middle Eastern countries and its historical, cultural, and political connections with the region.
What is the geographical position of Egypt?
Egypt is located in northeastern Africa, with its territory spanning both the African and Asian continents. The majority of Egypt’s land is in Africa, while the Sinai Peninsula connects it to Asia.
What is Egypt’s relationship with the Middle East?
Egypt has a long-standing relationship with the Middle East region. It is a founding member of the Arab League and has played a key role in various regional issues and conflicts, such as the Arab-Israeli conflict and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
What is the population and demographic profile of Egypt?
Egypt is the most populous country in the Middle East and the third most populous in Africa, with a population of over 100 million. The majority of Egyptians are young, with around 40% of the population aged between 10 and 20 years.
How is Egypt embracing digital transformation?
Egypt has witnessed significant growth in digital transformation in recent years, with around half of its population online. Improved infrastructure, cheaper data packages, and more affordable handsets are encouraging more Egyptians to come online.
What is the potential for fintech and e-commerce in Egypt?
Egypt’s growing digital ecosystem presents opportunities in the fintech and e-commerce sectors. The high rate of mobile penetration and the increasing adoption of digital financial services contribute to the development of the fintech market. The e-commerce market is also projected to grow significantly.
What role does Egypt play in the changing Middle East?
Egypt’s cooperative relationship with Israel and collaboration with other Arab states highlight a new dynamic in the Middle East. Egypt and its Sunni Arab partners share common concerns about Iran’s regional influence and the threat of jihadist groups, presenting opportunities for Egypt to play a significant role in shaping the future of the region.