Discover the fascinating world of the Red Sea, an aquatic wonderland known for its unique marine biodiversity and captivating ecosystems. With its rich history, vibrant coral reefs, and diverse marine life, the Red Sea offers an unparalleled experience for those seeking adventure and exploration.
Spanning an impressive area of about 438,000 square kilometers and stretching nearly 2,250 kilometers in length, the Red Sea boasts remarkable characteristics that set it apart. Located between Africa and Asia, this majestic body of water is bordered by Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen. Its name is derived from the red-colored cyanobacteria Trichodesmium erythraeum, which occasionally gives the water a reddish-brown hue.
The Red Sea’s geography is as diverse as its marine life. It is connected to the Mediterranean Sea via the man-made Suez Canal in the north, and to the Indian Ocean through the Bab el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden in the south. This strategic location makes the Red Sea an essential hub for global trade and transportation.
What makes the Red Sea truly remarkable is its remarkable formation. The Red Sea is the result of continental rifting, a geological process that began around 40 million years ago. This makes it one of the youngest oceans on Earth, constantly evolving and shaping its unique ecosystem.
One of the defining characteristics of the Red Sea is its high salinity levels. The combination of high evaporation, limited precipitation, minimal river inflow, and isolation from the rest of the Indian Ocean contributes to its distinct water composition. These factors create the perfect environment for the vibrant coral reefs and diverse marine species that call the Red Sea home.
Diving enthusiasts flock to the Red Sea to explore its extraordinary underwater world. With over 200 species of coral and a myriad of marine life, including endangered species like the dugong and the Green Sea Turtle, the Red Sea offers an unparalleled diving experience.
But the Red Sea isn’t just a natural wonder – it holds historical and religious significance as well. Throughout ancient times, it served as a vital trade route, connecting civilizations and facilitating the exchange of goods. It is also famously mentioned in biblical stories as the body of water that Moses parted to free the Israelites.
Whether you’re a nature lover, a history enthusiast, or an avid diver, the Red Sea offers something for everyone. Immerse yourself in the wonders of marine biodiversity and embark on an unforgettable journey through the depths of the Red Sea.
Origin of Its Name
The Red Sea derives its name from the unique phenomenon of a red-colored cyanobacteria called Trichodesmium erythraeum, which occasionally blooms on the water’s surface, resulting in a reddish-brown hue. This distinctive characteristic gave rise to the sea being universally known as the Red Sea.
The Red Sea Name Meaning
The name “Red Sea” is descriptive, referring to the coloration caused by Trichodesmium erythraeum. The red hue serves as a notable feature of this magnificent body of water, capturing the curiosity of marine enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Red Sea Cyanobacteria – Trichodesmium erythraeum
Trichodesmium erythraeum, commonly known as red cyanobacteria, is a marine microorganism responsible for the occasional bloom of red-colored water in the Red Sea. These cyanobacteria play a significant role in the ecological balance of the sea and contribute to the unique aquatic environment.
Geographical Location
The Red Sea is nestled between Africa and Asia, serving as a vital trade route and connecting multiple countries. It borders Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen. With its strategic location, the Red Sea acts as a gateway between two continents, making it an essential hub for international commerce and maritime transportation.
The geographical location of the Red Sea offers diverse opportunities for economic and cultural exchange. Its proximity to major markets in the Middle East and Africa enhances its significance as a maritime corridor. The sea’s borders with Egypt and Saudi Arabia provide access to two influential countries in the region, further adding to its importance as a geopolitical hub.
Here is a table summarizing the Red Sea’s geographical location and its neighboring countries:
| Country | Borders |
|---|---|
| Egypt | Northeastern border |
| Sudan | Eastern border |
| Eritrea | Northeastern border |
| Djibouti | Northern border |
| Saudi Arabia | Western border |
| Yemen | Southern border |
The Red Sea’s location between Africa and Asia, together with its neighboring countries, makes it an extraordinary and dynamic region, offering a combination of cultural, historical, and economic opportunities.

Size and Depth
The Red Sea is a vast body of water, covering an extensive area of approximately 438,000 square kilometers. It stretches nearly 2,250 kilometers in length, making it one of the longest seas in the world. The significant size of the Red Sea provides ample space for a diverse range of marine ecosystems to thrive.
Not only is the Red Sea expansive, but it is also known for its remarkable depth. With a maximum depth of 2,211 meters, the Red Sea ranks as one of the deepest seas globally. This depth creates unique habitats and supports a wide variety of marine species that have adapted to the challenging conditions.
| Attribute | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Size | Approximately 438,000 square kilometers |
| Length | Nearly 2,250 kilometers |
| Maximum Depth | 2,211 meters |
Diversity and Complexity
The significant size and depth of the Red Sea contribute to the diversity and complexity of its marine ecosystems. The vast expanse of water allows for a wide range of habitats, including coral reefs, seagrass beds, and rocky coasts, each supporting a unique array of marine life.
With its diverse and thriving ecosystems, the Red Sea offers scientists and researchers a wealth of opportunities to study and understand the intricate interactions between species and their environment.
Connection to Other Bodies of Water
The Red Sea, with its strategic location, is connected to other major bodies of water, making it an important hub for global maritime trade and transportation. Let’s explore the connections that link the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
Connection to the Mediterranean Sea
In the north, the Red Sea is connected to the Mediterranean Sea via the man-made Suez Canal. This artificial waterway, completed in 1869, provides a direct passage between the two seas, enabling ships to bypass the long and treacherous journey around the African continent.
Connection to the Indian Ocean
In the south, the Red Sea is linked to the Indian Ocean through two significant waterways. The Bab el-Mandeb Strait, located between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti in Africa, serves as the gateway to the Red Sea from the Gulf of Aden. This strait plays a crucial role in connecting the Red Sea with the vast expanse of the Indian Ocean.
Through the Gulf of Aden, which lies between Yemen and Somalia, the Red Sea opens up to the Indian Ocean, further extending its reach and facilitating maritime trade between countries in Asia, Africa, and beyond.
The connection of the Red Sea to both the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean creates a vital link in the global shipping network. It enables the transportation of goods, fuels economic growth, and fosters international trade. Moreover, these waterways have historical and cultural significance, serving as ancient trade routes, witnessing maritime exploration, and shaping the course of human history.

Formation of the Red Sea
The Red Sea, a stunning aquatic marvel, came into existence through the geological process of continental rifting. This phenomenon initiated around 40 million years ago, rendering the Red Sea one of the youngest oceans on Earth. Over time, this ongoing process continues to widen the Red Sea, shaping its awe-inspiring formation.
The continental rifting in the Red Sea occurs when tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface move away from each other, creating a rift. In the case of the Red Sea, this rift forms between the Arabian Plate and the Nubian Plate. As these plates separate, magma rises to the surface, leading to volcanic activity and the formation of new crust.
This process of continental rifting not only shapes the physical dimensions of the Red Sea but also influences its diverse marine ecosystems. The geological activity associated with the formation of the Red Sea contributes to its unique geographical features and supports the rich biodiversity found within its waters.
Salinity Levels
The Red Sea is renowned for its high salinity levels, which play a crucial role in shaping its unique ecosystem. The saltiness of the Red Sea is primarily influenced by several factors, including high evaporation rates, minimal precipitation, limited river inflow, and its isolation from the rest of the Indian Ocean.
The Red Sea experiences significant evaporation due to its warm climate and shallow depths, causing the water to become more saline. This evaporation process leaves behind salt, gradually increasing the concentration of dissolved salts in the sea. The lack of substantial rainfall in the region further contributes to the high salinity levels, as there is minimal freshwater input to dilute the seawater.
Additionally, the Red Sea’s limited river inflow exacerbates its saltiness. Unlike other seas and oceans, the Red Sea does not receive significant freshwater discharge from major rivers. As a result, the concentration of salts, including sodium, magnesium, calcium, and potassium, remains relatively high.
The Red Sea’s isolation from the Indian Ocean also plays a significant role in its high salinity levels. The limited exchange of water with the Indian Ocean hinders the dilution of salts, allowing the Red Sea to retain its distinct characteristics.
Overall, these factors combine to create a distinct water composition characterized by high salinity levels in the Red Sea. This unique environment supports the survival and thriving of a diverse array of marine life, including vibrant coral reefs, exotic fish species, and other remarkable organisms.
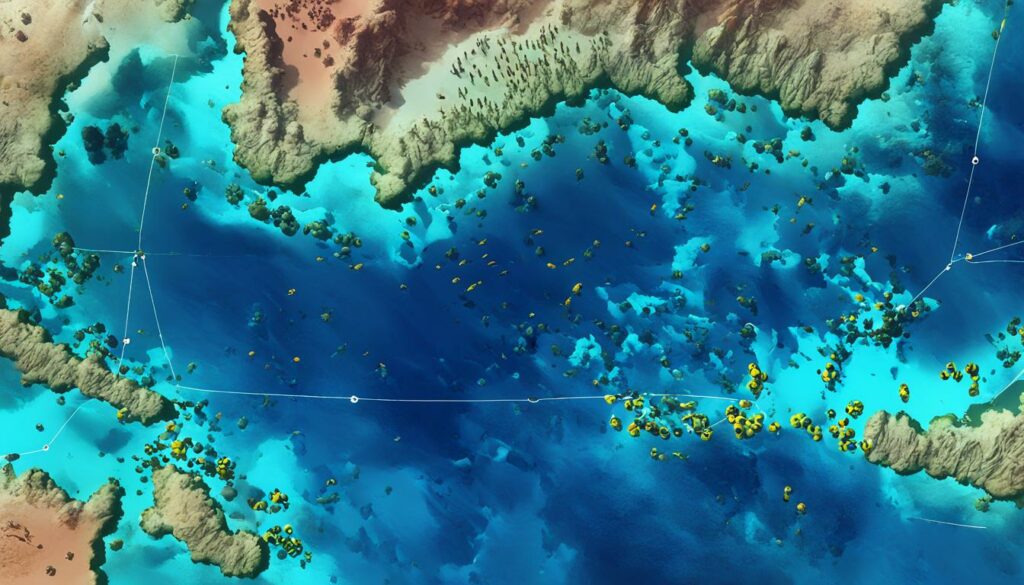
| Salinity Range | Salinity Level |
|---|---|
| Hypersaline Zones | >40 parts per thousand (ppt) |
| Outermost Zones | 36-40 ppt |
| Middle Zones | 34-36 ppt |
| Innermost Lagoonal Zones | 32-34 ppt |
Vibrant Coral Reefs
The Red Sea is renowned for its vibrant and diverse coral reefs, making it a paradise for underwater enthusiasts and nature lovers. With over 200 species of hard and soft coral, the Red Sea’s coral reef ecosystem is a true marvel of nature, teeming with life and vibrant colors.
These coral reefs not only provide breathtaking underwater landscapes but also serve as vital habitats for a wide range of marine life. From small colorful fish to majestic sea turtles and graceful manta rays, the coral reefs of the Red Sea are home to a multitude of species that rely on the reefs for protection, feeding grounds, and breeding sites.
The Red Sea’s coral reefs are essential components of its overall biodiversity. They contribute to the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem and play a crucial role in maintaining the health and sustainability of the surrounding waters. The reefs act as natural nurseries, supporting the growth and survival of countless organisms, and provide a source of food and shelter.
Exploring the Red Sea’s coral reefs is a truly awe-inspiring experience. Divers and snorkelers can witness the stunning beauty of the coral formations up close, with their intricate shapes and vibrant colors creating a mesmerizing underwater landscape. The Red Sea offers a wide range of dive sites, each with its own unique features and marine life, ensuring that there is something for every level of diving experience.
Coral Reef Conservation
Protecting the Red Sea’s coral reefs is of utmost importance to preserve their beauty and biodiversity for future generations. Various conservation efforts are in place to ensure the sustainable management of the reefs and minimize the impacts of human activities.
These initiatives include the establishment of marine protected areas, implementing regulations on fishing practices, and educating both locals and visitors about responsible diving and snorkeling behaviors. By promoting sustainable tourism and raising awareness about the importance of coral reef conservation, we can all play a part in preserving the Red Sea’s natural wonders.
| Coral Reef Species | Common Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|---|
| Brain Coral | Platygyra | Platygyra spp. |
| Finger Coral | Pocillopora | Pocillopora spp. |
| Staghorn Coral | Acropora | Acropora spp. |
| Mushroom Coral | Fungia | Fungia spp. |
| Soft Coral | Alcyonacea | Alcyonacea spp. |
Rich Marine Life
The Red Sea is a haven for diverse marine life, showcasing an abundance of species that thrive within its pristine waters. With over 1,000 invertebrate species and more than 1,200 species of fish, the Red Sea’s marine ecosystem teems with fascinating creatures, capturing the imagination of scientists, divers, and nature enthusiasts alike. From colorful corals to majestic pelagic species, the Red Sea offers a captivating underwater world to explore.
Endangered Species in the Red Sea
While the Red Sea is celebrated for its marine biodiversity, it is also home to several endangered and rare species. Preservation efforts are critical to protect these vulnerable creatures and maintain the delicate balance of the Red Sea’s ecosystem. Among the endangered species found in the Red Sea are:
- Dugong (Dugong dugon): These gentle giants, also known as sea cows, are herbivorous marine mammals that rely on seagrass habitats. They are at risk due to habitat loss and human activities such as pollution and accidental entanglement in fishing nets. Conservation initiatives aim to safeguard their habitats and promote sustainable fishing practices.
- Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas): The Red Sea provides crucial nesting sites for the endangered green sea turtle. The loss of nesting beaches, marine pollution, and accidental capture in fishing gear pose significant threats to their survival. Conservation efforts aim to protect nesting sites, raise awareness, and implement measures to reduce human impact on their habitats.
These endangered species highlight the need for conservation and sustainable practices to safeguard the Red Sea’s unique marine biodiversity for future generations.

| Species | Status |
|---|---|
| Dugong | Endangered |
| Green Sea Turtle | Endangered |
| Other marine species | Varied |
A Popular Diving Destination
The Red Sea is renowned for its breathtaking diving spots, attracting diving enthusiasts from around the globe. With its clear waters, vibrant coral reefs, and diverse marine life, it offers unforgettable experiences for both experienced divers and beginners.
Diving Spots in the Red Sea
The Red Sea boasts a wide range of diving spots that cater to different preferences and skill levels. Some of the popular diving spots in the Red Sea include:
- Ras Mohammed: Located at the tip of the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt, Ras Mohammed is known for its stunning coral gardens, steep walls, and abundant marine life. Divers can explore diverse ecosystems and encounter a variety of fish species, including barracudas, tuna, and reef sharks.
- The Brothers Islands: Situated about 60 kilometers off the coast of Egypt, the Brothers Islands offer thrilling drift dives and the opportunity to witness large pelagic species, such as hammerhead sharks and manta rays. The underwater scenery here is characterized by dramatic drop-offs and colorful coral formations.
- Elphinstone Reef: This reef, located near Marsa Alam in Egypt, is a hotspot for encounters with oceanic whitetip sharks. Its walls are covered in a rich tapestry of soft coral, attracting a diverse array of marine life, including schools of fish, turtles, and eels.
These are just a few examples of the many remarkable diving spots that the Red Sea has to offer. Each location provides a unique underwater experience, ensuring that divers of all levels can find something to suit their preferences.
Diving Tourism in the Red Sea
Diving tourism plays a significant role in the Red Sea’s economy, attracting a steady stream of visitors each year. The combination of world-class diving opportunities and the stunning natural beauty of the surrounding region makes the Red Sea an ideal destination for water sports enthusiasts.
| Factors contributing to diving tourism | Benefits for the local economy |
|---|---|
| The Red Sea’s clear and warm waters attract divers from different parts of the world. | Diving tourism generates revenue for local businesses, including dive centers, hotels, restaurants, and souvenir shops. |
| The diverse marine life and vibrant coral reefs provide unique diving experiences. | Job opportunities are created for local residents, such as dive instructors, boat captains, and underwater photographers. |
| The Red Sea’s accessibility, with numerous international airports and well-developed tourist infrastructure, makes it a convenient destination for divers. | It promotes the growth of infrastructure and services, improving the overall quality of life in surrounding communities. |
Overall, the Red Sea’s reputation as a premier diving destination continues to attract diving enthusiasts who seek to explore its underwater wonders and contribute to the local economy.
Historical and Religious Significance
The Red Sea holds a captivating blend of historical and religious importance. Dating back to ancient times, this legendary body of water played a crucial role in serving as a vital trade route for the transport of valuable spices and goods between the Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean. The Red Sea was a hub of commerce, connecting civilizations and fostering economic growth.
In religious narratives, the Red Sea is renowned for its pivotal role in the biblical account of Moses leading the Israelites to freedom. According to the story, with divine intervention, Moses parted the waters of the Red Sea, enabling the Israelites to escape the pursuing Egyptian army. This miraculous event continues to be a source of inspiration and awe for many.
Across generations, the Red Sea remains steeped in historical events and religious symbolism, enhancing its allure as a destination of profound significance. Today, visitors can explore the remnants of ancient trade routes and envision the tales of triumph and exploration that unfolded upon the sea’s shores. The rich tapestry of history and spirituality adds depth and meaning to the Red Sea, making it a truly remarkable and captivating destination.
FAQ
Q: What is the origin of the name “Red Sea”?
A: The Red Sea gets its name from the presence of a red-colored cyanobacteria called Trichodesmium erythraeum, which occasionally blooms on the water’s surface, giving it a reddish-brown color. Over time, this unique phenomenon led to the sea being referred to as the Red Sea.
Q: Where is the Red Sea located?
A: The Red Sea is located between Africa and Asia, with borders that include Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen. This seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean is nestled in a strategic location, connecting multiple countries and serving as a vital trade route.
Q: How large and deep is the Red Sea?
A: The Red Sea covers an extensive area of about 438,000 square kilometers and stretches nearly 2,250 kilometers in length. It is one of the world’s deepest seas, with a maximum depth of 2,211 meters. Its significant size and depth contribute to the diversity and complexity of its marine ecosystems.
Q: How is the Red Sea connected to other bodies of water?
A: The Red Sea is connected to the Mediterranean Sea via the man-made Suez Canal in the north. It is also connected to the Indian Ocean through the Bab el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden in the south. These connections to other bodies of water make the Red Sea an integral part of global maritime trade and transportation.
Q: How was the Red Sea formed?
A: The Red Sea is the result of a geological phenomenon known as continental rifting, which began approximately 40 million years ago. It is one of the youngest oceans on Earth, and the process of continental rifting continues to widen the Red Sea annually.
Q: Why does the Red Sea have high salinity levels?
A: The Red Sea is known for its high salinity levels, which contribute to its unique ecosystem. The saltiness of the Red Sea is a result of high evaporation, minimal precipitation, limited river inflow, and its isolation from the rest of the Indian Ocean. These factors create a distinct water composition that supports the Red Sea’s diverse marine life.
Q: What makes the Red Sea home to vibrant coral reefs?
A: The Red Sea is home to over 200 species of hard and soft coral, creating one of the most vibrant and diverse coral reef ecosystems in the world. These reefs not only provide breathtaking underwater landscapes but also serve as habitats for a wide range of marine life.
Q: What kind of marine life can be found in the Red Sea?
A: The Red Sea hosts an abundance of marine life, with over 1,000 invertebrate species and more than 1,200 species of fish. It is home to endangered and rare species such as the dugong and the Green Sea Turtle. The Red Sea’s diverse ecosystem supports a myriad of marine species, making it a haven for underwater biodiversity.
Q: Why is the Red Sea a popular destination for diving?
A: The Red Sea’s clear waters, vibrant coral reefs, and diverse marine life make it a sought-after destination for diving enthusiasts worldwide. Diving spots such as Ras Mohammed, the Brothers Islands, and Elphinstone Reef in Egypt are particularly popular among divers. The Red Sea’s unique underwater world offers unforgettable experiences and attracts tourists from all corners of the globe.
Q: Does the Red Sea have any historical or religious significance?
A: Yes, the Red Sea holds both historical and religious significance. Throughout ancient Egyptian, Greek, and Roman times, it served as a crucial trade route for spices and goods between the Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean. In biblical stories, the Red Sea is famously mentioned as the body of water that Moses parted to free the Israelites from the pursuing Egyptian army. Its rich history and religious importance add to the allure of the Red Sea as a fascinating destination.
